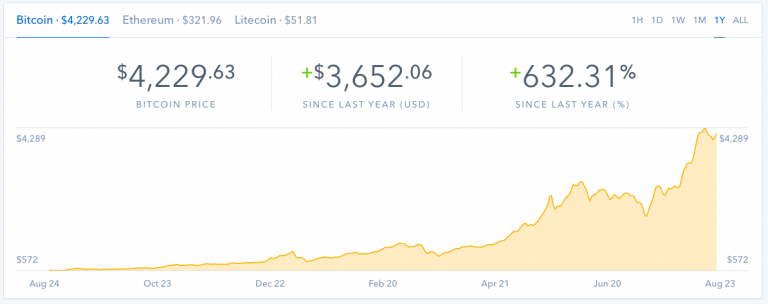
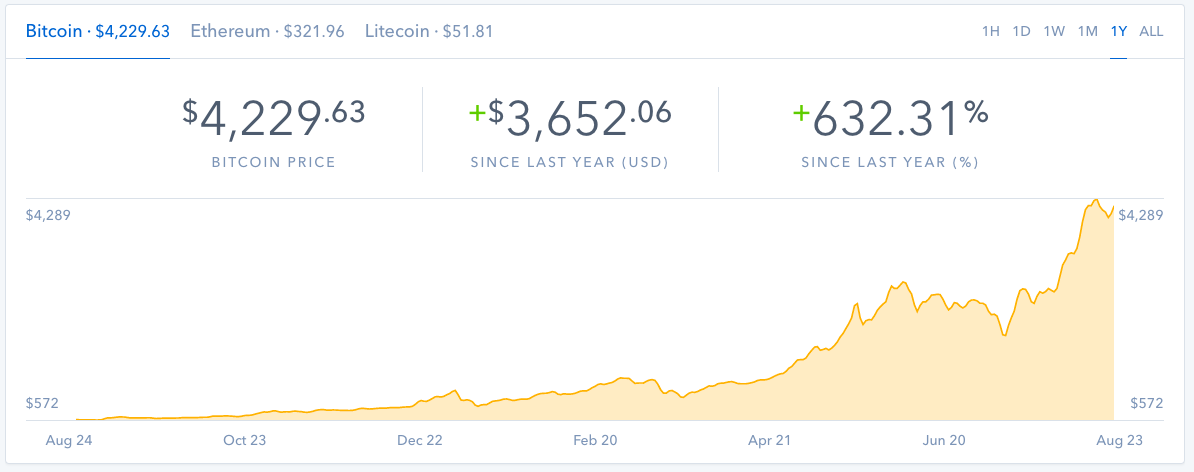
Bitcoin’s price volatility demands a reliable and informative ticker. This guide delves into the intricacies of Bitcoin price tickers, from their fundamental functions to the practical applications for investors and traders. We’ll explore how these tools display real-time data, track trends, and facilitate informed decisions within the cryptocurrency market.
Understanding the factors that drive Bitcoin’s price is crucial. This guide analyzes market sentiment, regulatory influences, and correlations with other financial assets, providing a holistic view of the dynamic forces at play. Different visualization techniques are also explored to aid in interpreting price patterns.
Introduction to Bitcoin Price Ticker
A Bitcoin price ticker is a real-time display of the current market price of Bitcoin. It provides a concise and readily accessible way to track the value of Bitcoin, crucial for investors and those interested in the cryptocurrency market. This dynamic display keeps users informed about the constantly fluctuating price.The primary function of a Bitcoin price ticker is to show the instantaneous price of Bitcoin in a chosen currency (e.g., USD, EUR).
Its purpose is to facilitate quick price comparisons and monitoring, aiding users in making informed decisions related to buying, selling, or holding Bitcoin. Its utility is paramount in a volatile market, enabling users to understand the current market conditions.
Bitcoin Price Ticker Formats
Bitcoin price tickers typically display the current price, often with a change indicator (e.g., up or down) and the percentage change. Some tickers also include the volume traded. The format is standardized across different platforms to provide a consistent user experience. This consistent presentation enables easy understanding and comparison across various sources. For instance, a ticker might show “$26,500.00 -0.3%” to indicate the current price of $26,500 and a decrease of 0.3% from the previous period.
Examples of Bitcoin Price Tickers
Different platforms offer various Bitcoin price tickers. On websites dedicated to cryptocurrency trading, these tickers often integrate seamlessly with charts and other market data. Mobile applications also provide Bitcoin price tickers, usually incorporated within a user interface for ease of access and to align with the mobile experience.
Comparison of Bitcoin Price Tickers
| Ticker |
Platform |
Features |
Accuracy |
| CoinMarketCap Ticker |
CoinMarketCap Website |
Real-time updates, historical price data, charts, and detailed market information. |
High |
| CoinGecko Ticker |
CoinGecko Website |
Real-time updates, comprehensive data on various cryptocurrencies, charts, and news. |
High |
| Binance Ticker |
Binance Exchange |
Real-time updates, integrated with trading platform, order book data, and trading volume. |
High |
| Crypto.com Ticker |
Crypto.com App |
Real-time updates, integrated with the user’s account, and customizable display options. |
High |
The table above compares different Bitcoin price tickers, highlighting their platforms, key features, and accuracy levels. Different tickers may focus on different aspects of the market, making them suitable for various user needs and preferences. High accuracy is a common feature among most platforms to ensure reliability for users.
Factors Influencing Bitcoin Price
Bitcoin’s price, a volatile yet captivating asset, is influenced by a complex interplay of market forces. Understanding these factors is crucial for investors and analysts alike to navigate the cryptocurrency market effectively. The price is not dictated by a single entity but rather a confluence of economic, technological, and social trends.
Market Sentiment
Market sentiment, encompassing investor confidence and public perception, plays a significant role in determining Bitcoin’s price. Positive sentiment often leads to increased demand and price appreciation, while negative sentiment can trigger selling pressure and price declines. Social media trends, news coverage, and prominent figures’ opinions all contribute to the overall market mood, impacting Bitcoin’s price direction. For instance, positive endorsements by influential figures can boost investor confidence, potentially leading to a surge in demand.
Conversely, negative news or regulatory concerns can lead to significant price drops.
Correlation with Other Financial Assets
Bitcoin’s price exhibits correlations with other financial assets, albeit not always consistently. Sometimes, Bitcoin’s price mirrors the movements of stocks or other cryptocurrencies, reflecting broader market trends. However, its unique characteristics and relative volatility often lead to periods of divergence from traditional financial markets. This correlation is not a fixed rule but rather a dynamic relationship that varies depending on the prevailing market conditions.
For example, during periods of market uncertainty, Bitcoin may act as a safe-haven asset, potentially increasing in value while other assets decline.
Impact of Regulatory Changes
Government regulations significantly impact the cryptocurrency market, including Bitcoin. Changes in regulations concerning taxation, trading, and mining can dramatically affect Bitcoin’s price. Favorable regulations, such as clearer guidelines on taxation or eased trading restrictions, can lead to increased investor confidence and price appreciation. Conversely, stricter regulations or regulatory uncertainty can cause selling pressure and price declines. The regulatory landscape varies considerably across jurisdictions, creating further complexity in understanding Bitcoin’s price movements.
Historical Impact of Events
The historical impact of various events on Bitcoin’s price highlights the complex interplay of factors influencing its volatility. Events such as major market crashes, regulatory announcements, or technological breakthroughs can significantly impact the price.
| Event |
Date |
Impact on Price |
Description |
| 2017 Bull Run |
Early 2017 |
Significant Increase |
A period of substantial price appreciation, driven by increased media attention and adoption by institutional investors. |
| 2018 Bear Market |
Mid 2018 |
Significant Decrease |
A period of significant price decline, influenced by regulatory concerns and market corrections. |
| COVID-19 Pandemic |
Early 2020 |
Mixed Impact |
Initial price drop followed by recovery as investors sought safe-haven assets. |
| China’s Ban on Crypto Mining |
2021 |
Significant Decrease |
Led to a substantial price drop as Chinese miners moved operations elsewhere. |
Analyzing Bitcoin Price Trends
Understanding Bitcoin’s price fluctuations requires a keen eye for patterns and trends. Price charts offer a visual representation of these movements, revealing insights into potential future price actions. Analyzing these trends can be valuable for informed investment decisions, but it’s crucial to remember that past performance is not indicative of future results.Interpreting Bitcoin price charts involves identifying key price levels, support and resistance zones, and recognizing distinct patterns.
These patterns, while not always predictable, often suggest potential price directions.
Interpreting Bitcoin Price Charts
Bitcoin price charts visually represent the price movement over time. Key components include the price axis (showing the value of Bitcoin), the time axis (showing the period covered, e.g., daily, weekly, monthly), and the price data points plotted on the graph. Understanding chart patterns and their significance can provide valuable insight into potential future price actions. The visual representation of price action reveals significant support and resistance levels, helping to identify possible reversal points.
Bitcoin Price Patterns
Various price patterns emerge in Bitcoin’s price history. These patterns, while not definitive predictions, often suggest potential price movements.
Bull Run
A bull run in Bitcoin is characterized by a sustained period of increasing prices. This phase is often marked by strong buying pressure, with investors anticipating further price appreciation. Examples include the 2017 bull run and the recent bull runs following significant price corrections. This pattern often signifies increased investor confidence and adoption, with anticipation for continued growth.
Bear Market
A bear market in Bitcoin is defined by a sustained period of decreasing prices. During this period, selling pressure typically outweighs buying pressure. Fear and uncertainty often accompany bear markets, as investors anticipate further price declines. Examples include the 2018-2019 bear market and more recent bear markets. A decline in investor confidence and reduced demand are usually observed.
Other Price Patterns
Other price patterns frequently observed include consolidation phases, where prices fluctuate within a defined range, and breakout patterns, signifying a potential directional shift. These patterns can help to anticipate potential price movements.
Comparison of Bitcoin Price Patterns
| Pattern |
Description |
Example |
Interpretation |
| Bull Run |
Sustained period of increasing prices. |
2017, recent post-correction rallies. |
High investor confidence, anticipation of continued growth. |
| Bear Market |
Sustained period of decreasing prices. |
2018-2019, recent downturns. |
Selling pressure outweighs buying pressure, fear and uncertainty. |
| Consolidation |
Prices fluctuate within a defined range. |
Periods between significant price swings. |
Market is evaluating direction, potential for breakout. |
| Breakout |
Significant price movement beyond a defined range. |
Sudden price increases or decreases following a consolidation. |
Potential for a sustained trend shift. |
Cryptocurrency Market Overview
The cryptocurrency market is a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector, characterized by significant price fluctuations and a complex interplay of factors. It encompasses a diverse range of digital assets, each with unique characteristics and functionalities. Understanding this market requires a comprehensive view of its components and the intricate relationships between its various players.The cryptocurrency market is interconnected, with Bitcoin often serving as a benchmark for other cryptocurrencies.
Fluctuations in Bitcoin’s value often trigger similar movements in the broader cryptocurrency market. However, individual cryptocurrencies can exhibit independent price action, influenced by factors specific to their respective projects and communities.
Relationship Between Bitcoin and Other Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin’s dominance in the market often impacts the performance of other cryptocurrencies. A strong Bitcoin price generally correlates with a positive trend in the overall cryptocurrency market, while a decline in Bitcoin’s value can lead to a broader market downturn. This relationship is not always absolute, though, as factors specific to individual cryptocurrencies can cause deviations from this general trend.
Comparison of Bitcoin with Prominent Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin, the pioneering cryptocurrency, is distinguished by its decentralized nature and secure transaction mechanisms. Other prominent cryptocurrencies, like Ethereum, Litecoin, and Ripple, offer alternative features and functionalities. Ethereum, for instance, is known for its smart contract capabilities, empowering decentralized applications. Litecoin, a fork of Bitcoin, emphasizes faster transaction speeds. Ripple focuses on facilitating cross-border payments.
These distinctions highlight the variety within the cryptocurrency market, allowing investors to choose digital assets aligned with their investment objectives.
Historical Evolution of the Cryptocurrency Market
The cryptocurrency market’s evolution is marked by phases of rapid growth, consolidation, and correction. Early adoption and technological advancements propelled initial growth, while subsequent market volatility and regulatory scrutiny have shaped the landscape. The history of the cryptocurrency market reveals the importance of understanding the cyclical nature of the industry and the long-term potential for innovation. For instance, the 2017 bull run followed by the 2018 bear market exemplifies the cyclical nature of this market.
Key Characteristics of Various Cryptocurrencies
Understanding the distinct characteristics of various cryptocurrencies provides insight into their potential applications and investment prospects. The table below highlights key characteristics of some prominent cryptocurrencies.
| Cryptocurrency |
Symbol |
Market Cap (USD) |
Description |
| Bitcoin |
BTC |
(Data from reliable source needed) |
Decentralized digital currency, pioneering cryptocurrency. |
| Ethereum |
ETH |
(Data from reliable source needed) |
Decentralized platform for applications and smart contracts. |
| Litecoin |
LTC |
(Data from reliable source needed) |
Fork of Bitcoin, emphasizing faster transaction speeds. |
| Ripple |
XRP |
(Data from reliable source needed) |
Facilitates cross-border payments. |
| Solana |
SOL |
(Data from reliable source needed) |
High-throughput blockchain platform. |
Note: Market capitalization data is crucial but needs to be updated with precise values from current reliable sources.
Technical Analysis of Bitcoin Price
Technical analysis is a crucial tool for understanding and potentially predicting Bitcoin price movements. It focuses on historical price and volume data to identify patterns and trends, rather than relying on fundamental factors like market sentiment or economic indicators. By recognizing these patterns, traders can make informed decisions about buying or selling Bitcoin.
Methods Used in Bitcoin Price Prediction
Technical analysis employs various methods to predict Bitcoin price movements. These methods often involve identifying recurring patterns in price charts, which are then used to project future price actions. Key methods include examining moving averages, support and resistance levels, and volume analysis. These techniques, when used effectively, can provide valuable insights into the potential trajectory of Bitcoin’s price.
Moving Averages
Moving averages are crucial indicators in technical analysis. They smooth out price fluctuations to reveal underlying trends. A simple moving average (SMA) calculates the average price over a specific period. A longer period SMA typically highlights the overall trend, while a shorter period SMA often reveals more short-term price changes. Using a Bitcoin price ticker, traders can observe real-time SMA values alongside the current price, aiding in identifying trend direction.
For example, a 200-day SMA consistently above the current price often signals an uptrend.
Support and Resistance Levels
Support and resistance levels are horizontal price levels where prices have historically tended to reverse. Support levels represent price levels where buyers typically step in, while resistance levels mark price points where sellers often dominate. Identifying these levels from a Bitcoin price ticker enables traders to anticipate potential price reversals and set appropriate entry and exit points. For instance, if the price repeatedly bounces off a specific resistance level, it suggests a potential hurdle for further upward movement.
Volume Analysis
Volume analysis assesses the trading volume associated with price movements. High volume during a price surge often indicates strong conviction in the direction of the trend. Conversely, low volume during a price move suggests a lack of significant interest, potentially signaling a less significant price change. A Bitcoin price ticker showing real-time volume data alongside price charts is vital for analyzing the strength behind price movements.
For example, a sudden surge in volume accompanying a price increase suggests heightened investor interest and potentially more substantial upward momentum.
Importance of Risk Management
Risk management is paramount in technical analysis. No technical analysis method guarantees accurate predictions. Therefore, traders should use technical analysis alongside other factors and always define stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. Understanding the inherent risks associated with Bitcoin trading is crucial for effective risk management.
Technical Indicators for Monitoring Bitcoin Price Trends
| Indicator |
Description |
Interpretation |
Example |
| Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) |
Measures the momentum of price changes. |
Crossovers of the MACD lines often signal potential trend changes. |
A bullish crossover indicates potential upward momentum. |
| Relative Strength Index (RSI) |
Measures the strength of price movements. |
Overbought or oversold conditions can suggest potential price reversals. |
An RSI reading above 70 may suggest an overbought condition. |
| Bollinger Bands |
Measures price volatility and potential price ranges. |
Bands expanding or contracting indicate potential volatility shifts. |
Narrowing bands can suggest a potential price consolidation. |
| Volume |
Shows trading volume associated with price changes. |
High volume often signifies strong conviction. |
High volume during a price increase suggests heightened investor interest. |
Practical Application of Bitcoin Price Ticker Data
Bitcoin price tickers provide real-time data, crucial for investors and traders. Understanding how to utilize this data effectively can significantly impact investment strategies and profitability. This section details the practical applications of Bitcoin price ticker data, focusing on its use in investment decisions, trade execution, portfolio management, and analysis.Real-time price information, combined with other market data, empowers informed decision-making in the dynamic cryptocurrency market.
Traders can leverage this information to adjust their strategies in response to rapid price fluctuations.
Investment Decisions
Bitcoin price tickers are essential tools for investors looking to make informed decisions. By tracking price movements and volume, investors can identify potential entry and exit points, aiding in maximizing returns. The price ticker provides a snapshot of current market sentiment, which can be a key factor in evaluating investment opportunities. Careful monitoring of price trends, combined with fundamental and technical analysis, helps investors make calculated choices.
Trade Execution
Traders use Bitcoin price tickers to execute trades efficiently. The real-time data allows for quick responses to market changes, enabling traders to capitalize on opportunities and manage risk effectively. Alerts generated by tickers can signal potential entry or exit points, helping traders avoid missing profitable trades. Price tickers are indispensable for executing trades, especially during periods of high volatility.
Portfolio Management
Bitcoin price tickers play a critical role in portfolio management. Tracking Bitcoin’s price allows investors to assess the performance of their Bitcoin holdings within their overall portfolio. This data helps investors adjust their portfolio allocation based on market conditions and individual risk tolerance. The price data, combined with other portfolio holdings, facilitates a comprehensive view of investment performance.
Analysis of Bitcoin Price Data
Analyzing Bitcoin price ticker data can reveal valuable insights. Identifying patterns, trends, and correlations with other market indicators allows for better understanding of market dynamics. For example, observing price spikes alongside news events can help understand market sentiment and its influence on price. Visualizing price charts, often provided by the tickers, can reveal patterns and potential support/resistance levels.
Examples of Using Bitcoin Price Ticker Data for Analysis
A trader observes a consistent upward trend in Bitcoin’s price alongside increased trading volume. This suggests increasing investor confidence and potentially a continuation of the upward trend. Alternatively, a sharp price drop following a regulatory announcement can signal a period of uncertainty, prompting the trader to review their investment strategy.
Summary Table
| Application |
Description |
Benefit |
Example |
| Investment Decisions |
Identifying entry/exit points, assessing market sentiment. |
Maximizing returns, mitigating risk. |
Buying Bitcoin when price is low and expected to rise. |
| Trade Execution |
Quick response to market changes, utilizing alerts. |
Capitalizing on opportunities, managing risk. |
Exiting a position when price drops below a predefined threshold. |
| Portfolio Management |
Assessing Bitcoin’s performance within the portfolio, adjusting allocation. |
Maintaining portfolio balance, adapting to market conditions. |
Reducing Bitcoin holdings if the overall portfolio is becoming overexposed. |
| Price Analysis |
Identifying patterns, trends, correlations with other indicators. |
Understanding market dynamics, making informed decisions. |
Observing price spikes after news announcements to gauge market sentiment. |
Bitcoin Price Ticker Visualization
Visualizing Bitcoin price data effectively is crucial for understanding trends and making informed decisions. Clear and informative visualizations transform raw data into easily digestible insights, allowing users to quickly grasp price fluctuations, patterns, and potential future movements. This section details various visualization techniques suitable for Bitcoin price data.
Different Visualization Types
Various chart types can effectively represent Bitcoin price data. Choosing the right visualization depends on the specific insights sought and the context of the analysis. Line charts, bar charts, candlestick charts, and even scatter plots can be used to highlight different aspects of Bitcoin’s price behavior.
Line Charts
Line charts are excellent for displaying price trends over time. They show the evolution of Bitcoin’s value across a period, making it easy to spot upward or downward movements and identify significant price fluctuations. This visual representation simplifies the understanding of overall price trends, enabling an assessment of Bitcoin’s price journey.
Bar Charts
Bar charts can highlight price comparisons across different time periods or categories. For instance, they can visually compare Bitcoin’s price with other cryptocurrencies or with traditional assets over time. This visual format facilitates the comparison of Bitcoin’s performance against benchmarks.
Candlestick Charts
Candlestick charts provide a detailed view of price movements over a specified time frame. Each candlestick represents an opening, closing, high, and low price for a particular period, enabling a comprehensive overview of price action and volatility. This method is popular among technical analysts due to its visual representation of price action, including trends, patterns, and support/resistance levels.
Scatter Plots
Scatter plots can illustrate the relationship between Bitcoin’s price and other variables, such as the volume of transactions or market sentiment. By plotting these variables against each other, one can potentially identify correlations or patterns in the data. This method allows for the identification of potential relationships between Bitcoin’s price and external factors.
Interactive Visualizations
Interactive visualizations, often implemented using JavaScript libraries, enhance the user experience. These dynamic charts allow users to zoom, pan, and filter data to focus on specific time periods or aspects of the price action. The interactivity enables users to explore Bitcoin price data in greater detail and tailor their analysis to specific interests. Examples include interactive candlestick charts that allow users to select different timeframes, revealing more granular details of price movements.
Chart Comparison Table
| Chart Type |
Description |
Suitability for Bitcoin Data |
Example |
| Line Chart |
Displays price trends over time. |
Excellent for showing overall price movement. |
Bitcoin price from 2017 to 2023, showcasing general upward trend with volatility. |
| Bar Chart |
Compares prices across categories. |
Suitable for comparing Bitcoin to other cryptocurrencies or assets. |
Bitcoin price vs. Ethereum price over a year, highlighting relative performance. |
| Candlestick Chart |
Detailed view of price action over time. |
Ideal for technical analysis, showing open, close, high, and low prices. |
Bitcoin candlestick chart for a week, highlighting daily price fluctuations. |
| Scatter Plot |
Shows relationships between variables. |
Useful for exploring correlations between Bitcoin price and other factors. |
Bitcoin price vs. trading volume, revealing potential correlation. |
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, this comprehensive guide to Bitcoin price tickers has provided a thorough understanding of their functionalities and practical applications. From technical analysis to portfolio management, we’ve examined how these tools empower investors and traders to navigate the complex cryptocurrency landscape. The information presented offers a solid foundation for anyone seeking to interpret Bitcoin price data effectively.
FAQ
What are some common chart types used to visualize Bitcoin price data?
Line charts, bar charts, candlestick charts, and area charts are common choices. The best choice depends on the specific information you want to convey.
How can I use a Bitcoin price ticker to make investment decisions?
A ticker provides real-time price data, which helps traders identify potential entry or exit points. Combining this with technical analysis can improve investment strategies.
What is the role of market sentiment in influencing Bitcoin price?
Market sentiment, the collective mood and outlook of investors, significantly impacts Bitcoin’s price. Positive sentiment generally leads to price increases, while negative sentiment often results in price drops.
What is the relationship between Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies?
Bitcoin, as the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, often acts as a benchmark for other cryptocurrencies. Price movements in Bitcoin can influence the prices of other cryptocurrencies, but there are often independent factors affecting individual coins.