Bitcoin’s price reaching zero is a hypothetical yet compelling scenario with significant implications for the cryptocurrency market. This exploration delves into the theoretical underpinnings of such a drastic price drop, considering various factors from technological advancements to regulatory changes.
Examining the historical volatility of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies provides context, allowing us to assess the likelihood of a complete devaluation. This analysis will also compare Bitcoin’s potential fate with traditional financial assets.
Bitcoin Price at Zero
A Bitcoin price of zero, while seemingly improbable, presents a fascinating theoretical exercise. Exploring the potential scenarios and cascading effects of such a drastic devaluation reveals crucial insights into the vulnerabilities and resilience of the cryptocurrency market. Understanding the factors that could lead to this outcome is vital for investors and stakeholders to assess the potential risks and opportunities within the digital asset landscape.A Bitcoin price of zero signifies a complete loss of faith and utility in the cryptocurrency.
This catastrophic event would stem from a confluence of factors, ranging from technological failures to severe regulatory crackdowns and profound economic downturns. Each factor plays a significant role in eroding Bitcoin’s value, ultimately leading to its perceived worthlessness.
Theoretical Model for Bitcoin Price Collapse
The collapse of Bitcoin’s price to zero hinges on the erosion of its core value propositions. This involves a breakdown of trust, technological obsolescence, or significant regulatory hurdles. A critical loss of user confidence and widespread adoption, coupled with economic crises, can severely impact the value proposition.
Factors Contributing to Bitcoin’s Zero Value
Several interconnected factors could lead to Bitcoin’s complete devaluation. Technological vulnerabilities, like a major security breach or a significant protocol flaw, could cripple the network’s functionality. Economic downturns, such as hyperinflation or a major financial crisis, could diminish the perceived value of Bitcoin as a store of value. Regulatory crackdowns, particularly in jurisdictions where Bitcoin is heavily used, could severely curtail the cryptocurrency’s accessibility and utility.
Consequences of a Bitcoin Price Reaching Zero
The implications of a Bitcoin price reaching zero are far-reaching. Investors would face substantial losses, potentially triggering a ripple effect throughout the financial system. Businesses reliant on Bitcoin for transactions or investments would be severely impacted, with potentially devastating consequences for their operations. The overall cryptocurrency market would experience a major setback, possibly leading to a period of stagnation or even collapse, potentially impacting other digital assets.
Impact on Investors, Businesses, and the Financial System
The loss of Bitcoin’s value would cause significant losses for investors who hold Bitcoin. Businesses that have integrated Bitcoin into their operations would face substantial operational disruption. The wider financial system could also experience repercussions, including a decline in investor confidence and a possible decrease in market liquidity. The extent of the impact depends on the speed and severity of the price collapse.
Comparative Analysis of Zero-Price Scenarios
| Scenario | Cause | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Technological Failure | Major security breach, crippling protocol flaw, or widespread network disruption. | Loss of user confidence, cessation of transactions, rendering the currency unusable. |
| Regulatory Crackdown | Stricter regulations, outright bans, or severe penalties in major jurisdictions. | Limited accessibility, restrictions on usage, and a significant reduction in trading volume. |
| Economic Collapse | Hyperinflation, major financial crisis, or a collapse in the global economy. | Loss of trust as a store of value, diminishing its utility in times of economic instability. |
| Massive Adoption Failure | Lack of widespread adoption, limited use cases, or a lack of mainstream acceptance. | Limited utility, a significant reduction in trading volume, and a drop in perceived value. |
Historical Context of Cryptocurrency Price Volatility
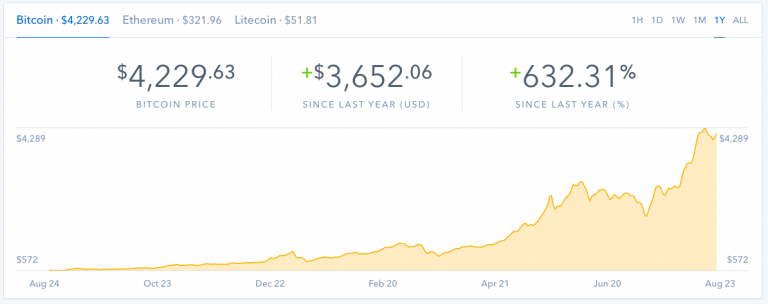
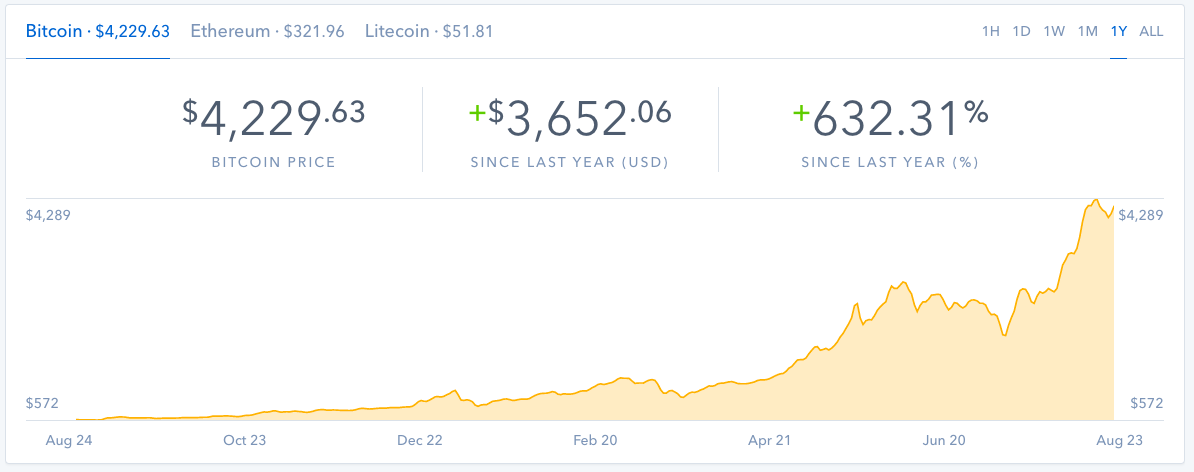
Bitcoin, and the broader cryptocurrency market, are notorious for their extreme price fluctuations. This volatility, often characterized by rapid and dramatic price swings, has significantly impacted investor sentiment and market participation. Understanding this historical context is crucial for assessing the risks and opportunities within the cryptocurrency space.The inherent nature of cryptocurrency markets, characterized by limited regulatory oversight and decentralized control, contributes to price instability.
This dynamic environment, combined with the relative novelty of digital currencies, has resulted in considerable price volatility over the years. The market’s susceptibility to speculative activity and sudden shifts in investor sentiment further exacerbates these fluctuations.
Bitcoin Price Fluctuations Over Time
The history of Bitcoin’s price is marked by periods of significant growth and sharp declines. Early adopters and investors often experienced substantial gains, but these gains were frequently followed by significant losses as market sentiment shifted. Several notable events, including regulatory developments, technological advancements, and major market events, have influenced Bitcoin’s price.
Notable Price Crashes and Recoveries
Several notable crashes and recoveries have shaped the cryptocurrency market’s history. The 2017-2018 bull run, followed by a steep decline, is a prime example. Factors like regulatory uncertainty, market corrections, and investor sentiment shifts contributed to these price movements. Similarly, the 2022 market downturn saw significant declines in numerous cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, driven by factors such as tightening monetary policies, macroeconomic headwinds, and concerns about the sustainability of some crypto projects.
These crashes, while painful, are part of the inherent volatility of the market and often pave the way for future growth and innovation.
Correlation with Other Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin, often considered the leading cryptocurrency, tends to exhibit a degree of correlation with other cryptocurrencies. Major movements in Bitcoin’s price often trigger similar reactions in other cryptocurrencies. However, this correlation isn’t absolute, and individual cryptocurrencies can display unique price actions influenced by their specific characteristics and project-specific events. The degree of correlation can vary depending on the specific market conditions and the relationship between the cryptocurrency in question and Bitcoin.
Comparison to Traditional Assets
Bitcoin’s volatility stands in stark contrast to traditional assets like stocks and bonds. Stocks and bonds, while subject to market fluctuations, generally exhibit less extreme price swings than Bitcoin. The significantly higher volatility of Bitcoin necessitates a more cautious investment approach, especially for those unfamiliar with the risks associated with cryptocurrencies. This difference in volatility is a key factor in the decision-making process for investors.
Factors Contributing to Bitcoin’s Price Fluctuations
Numerous factors influence Bitcoin’s price, including:
- Market Sentiment and Speculation: Investor confidence and speculation play a substantial role in determining Bitcoin’s price. Positive sentiment often leads to price increases, while negative sentiment can trigger sharp declines.
- Regulatory Developments: Government regulations and policies concerning cryptocurrencies can significantly impact market confidence and, consequently, Bitcoin’s price. Changes in regulations often lead to price fluctuations, as investors react to the potential impact on the market.
- Technological Advancements: New technologies and advancements in the blockchain space can either bolster or hinder Bitcoin’s adoption and price. Innovative implementations often lead to price growth, while setbacks can lead to price declines.
- Major Market Events: Global economic conditions, geopolitical events, and significant news events can affect market sentiment and, in turn, Bitcoin’s price. The market often reacts to such events, leading to fluctuations in price.
Historical Highs and Lows of Bitcoin
| Year | High (USD) | Low (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 64,800 | 30,000 |
| 2022 | 48,000 | 15,000 |
| 2023 | 30,000 | 16,000 |
Note
Values are approximate and can vary based on the specific data source. Historical data should be used for informational purposes only and not as a basis for investment decisions.*
Cryptocurrency Fundamentals in Relation to Bitcoin
Cryptocurrencies, a novel form of digital money, are built on decentralized principles, operating independently of traditional financial institutions. Their value and use depend heavily on underlying technologies and market dynamics. Bitcoin, the pioneering cryptocurrency, has significantly influenced the broader cryptocurrency landscape. Understanding the fundamentals of these digital assets is crucial to comprehending their potential and risks.
Fundamental Principles of Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual currencies designed to work as a medium of exchange, similar to traditional fiat currencies. Their core principle lies in decentralization, meaning they operate without a central bank or governing body. Transactions are verified and recorded on a distributed ledger, known as a blockchain, ensuring transparency and security. This decentralization, however, also introduces challenges in terms of regulation and oversight.
Blockchain Technology and Its Role
Blockchain technology is the foundation upon which most cryptocurrencies are built. It’s a distributed, immutable ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. This decentralized nature makes it resistant to tampering and fraud. Each transaction is grouped into a “block,” linked to the previous block in a chronological chain. This cryptographic linking ensures the integrity and transparency of the records.
The security of blockchain is based on cryptography, ensuring that transactions are secure and verifiable.
Different Types of Cryptocurrencies and Their Characteristics
A wide array of cryptocurrencies exist beyond Bitcoin, each with unique characteristics and intended uses. Some are designed for specific purposes, like decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, while others focus on enhanced scalability or security. The diversity of cryptocurrencies reflects the evolving needs and aspirations within the digital asset space. Their characteristics vary significantly, impacting their use cases and market performance.
Key Differences Between Bitcoin and Other Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, pioneered the concept of decentralized digital money. While other cryptocurrencies share some similarities, key differences exist in their underlying technologies, transaction speeds, scalability, and intended use cases. These differences influence their individual market dynamics and appeal to specific user groups.
Cryptocurrency List with Bullet Points
- Bitcoin (BTC): The original cryptocurrency, known for its security and limited supply. Bitcoin’s primary function is as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system.
- Ethereum (ETH): A platform for decentralized applications (dApps), allowing for the creation of smart contracts and other blockchain-based services. Ethereum is primarily used for its smart contract functionality.
- Litecoin (LTC): Designed as a faster and more scalable alternative to Bitcoin, focusing on quicker transaction speeds. It prioritizes transaction speed over other factors.
- Ripple (XRP): A cryptocurrency primarily focused on cross-border payments, emphasizing speed and efficiency in financial transactions. Ripple’s primary use case is facilitating cross-border transactions.
- Tether (USDT): A stablecoin pegged to the US dollar, aiming to provide price stability and facilitate easier trading. Tether’s main function is to maintain a stable value.
Key Characteristics of Bitcoin and Other Prominent Cryptocurrencies
| Cryptocurrency | Mechanism | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin (BTC) | Proof-of-work consensus mechanism, limited supply of 21 million coins. | Digital currency, peer-to-peer electronic cash system. |
| Ethereum (ETH) | Proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, smart contract platform. | Decentralized applications (dApps), smart contracts. |
| Litecoin (LTC) | Proof-of-work consensus mechanism, faster transaction times. | Alternative payment method, faster transactions than Bitcoin. |
| Ripple (XRP) | Consensus mechanism based on a different model than Bitcoin or Ethereum. | Cross-border payments, international transactions. |
| Tether (USDT) | Stablecoin pegged to the US dollar. | Maintaining a stable value, facilitating easier trading. |
Potential Scenarios for a Bitcoin Price of Zero
Bitcoin’s price volatility has always been a defining characteristic of the cryptocurrency market. While a price of zero for Bitcoin is an extreme outcome, understanding potential scenarios helps contextualize the inherent risks associated with this nascent asset class. Analyzing these scenarios is crucial for investors to assess their risk tolerance and make informed decisions.A price of zero for Bitcoin would represent a catastrophic failure of the cryptocurrency’s underlying value proposition.
Such a collapse would be driven by a confluence of factors, ranging from fundamental flaws in the technology to external shocks impacting market confidence.
Triggers for a Substantial Drop in Bitcoin’s Value
A significant drop in Bitcoin’s value, potentially leading to a price of zero, can be triggered by several factors. Market manipulation, regulatory crackdowns, and fundamental weaknesses in the underlying technology all pose substantial risks. Understanding these catalysts is vital for investors to assess their exposure and manage their risk.
- Regulatory Actions: Stringent regulatory measures, such as outright bans or restrictions on transactions, can severely cripple Bitcoin’s adoption and usage. For example, if major financial institutions and governments globally restricted or prohibited Bitcoin transactions, this could lead to a drastic decrease in demand and consequently, a significant price drop. The fear of legal repercussions and the removal of institutional backing would quickly undermine confidence and potentially cause a collapse.
- Widespread Systemic Failures: The Bitcoin network, like any other decentralized system, is vulnerable to failures. A significant security breach or a major attack on the network’s integrity could cause irreparable damage, severely impacting its trustworthiness and value.
- Technological Obsolescence: Bitcoin’s technology might be overtaken by more innovative and efficient alternatives. If superior blockchain technologies emerge with broader applicability and stronger security, Bitcoin’s relevance could diminish rapidly. The introduction of a better-performing or more user-friendly cryptocurrency could render Bitcoin obsolete and cause its price to plummet.
- Market Manipulation: A coordinated effort to manipulate the market, either by short-selling or artificially suppressing demand, could significantly impact Bitcoin’s price. Such manipulation could be orchestrated by large entities or coordinated groups seeking to profit from the decline.
Impact of Regulatory Actions or Market Manipulation
Regulatory actions and market manipulation can significantly impact Bitcoin’s price. These external forces can cause substantial price drops and even potentially push Bitcoin’s price to zero.
- Regulatory Crackdowns: Government regulations or bans on Bitcoin transactions, similar to the historical actions taken against certain financial instruments, can effectively eliminate Bitcoin’s use as a means of exchange. This would greatly reduce demand, impacting the market value. This is not hypothetical. Several countries have either banned or heavily restricted Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
- Market Manipulation Strategies: Sophisticated market manipulation, involving coordinated short-selling or spreading misinformation, could destabilize the market. This has been observed in traditional markets and can equally impact the volatile cryptocurrency space.
Outcomes if a Significant Portion of Bitcoin’s Supply Becomes Worthless
If a substantial portion of Bitcoin’s supply becomes worthless, the social and economic ramifications would be considerable.
Scenario 1: A catastrophic security breach or a major attack on the Bitcoin network’s integrity could render a significant portion of Bitcoin’s supply worthless. The trust and confidence in the system would be lost, and the price would likely plummet to zero.
Scenario 2: A widespread adoption of a competing cryptocurrency with superior technology could render Bitcoin obsolete. This would significantly reduce demand, potentially driving the price to zero.
Scenario 3: A complete ban or heavy regulation of Bitcoin transactions in major jurisdictions could cripple its use as a currency or store of value, leading to a price collapse.
Social and Economic Ramifications
The social and economic implications of a Bitcoin price approaching zero would be substantial.
- Loss of Investor Confidence: A price collapse would severely damage investor confidence in the cryptocurrency market, potentially deterring future investment and innovation.
- Economic Instability: A widespread loss of value in Bitcoin assets would have a ripple effect on the broader economy, impacting financial markets and investor portfolios.
- Social Disruption: If Bitcoin is widely used as a payment method, its devaluation could disrupt social and economic systems, especially in regions where it has been adopted as a currency.
Alternative Perspectives on Bitcoin’s Future
Bitcoin’s future trajectory remains a subject of intense debate, with a spectrum of opinions ranging from optimistic projections to pessimistic forecasts. The cryptocurrency’s journey has been marked by significant price fluctuations and evolving market dynamics, leading to varied interpretations of its long-term viability. Understanding these differing viewpoints is crucial to evaluating Bitcoin’s potential role in the future of finance.Alternative perspectives on Bitcoin’s future are driven by diverse assessments of its technological merits, market acceptance, and regulatory landscape.
These diverse viewpoints highlight the complexity of evaluating a decentralized asset with inherent volatility and a constantly evolving regulatory environment.
Diverse Opinions on Long-Term Prospects
Various experts hold differing views on Bitcoin’s long-term potential. Some believe that Bitcoin’s unique characteristics, such as its scarcity and decentralized nature, position it as a promising investment and a valuable store of value. Others maintain that Bitcoin’s inherent volatility and susceptibility to market manipulation make it a high-risk investment. These contrasting opinions reflect the inherent uncertainty surrounding the cryptocurrency’s future.
Alternative Viewpoints on Bitcoin’s Financial Role
Bitcoin’s potential role in the financial world is subject to diverse interpretations. Proponents envision Bitcoin as a disruptive force, potentially challenging traditional financial systems and offering alternative payment solutions. Conversely, critics argue that Bitcoin’s volatility and lack of regulatory oversight pose significant risks to its adoption as a mainstream financial instrument.
Expert Opinions on Likelihood of Price Reaching Zero
Experts’ assessments of the likelihood of Bitcoin’s price reaching zero vary considerably. Some analysts believe that Bitcoin’s price is likely to experience further declines, potentially reaching lower levels. However, others assert that Bitcoin’s underlying technology and potential applications in various sectors will prevent its complete devaluation. A critical evaluation of these divergent opinions is vital for assessing Bitcoin’s future.
Arguments for and Against Bitcoin’s Survival
Arguments for Bitcoin’s survival often center on its potential as a decentralized store of value, its use as a medium of exchange, and its potential for use in various applications. Conversely, arguments against Bitcoin’s survival often cite its volatility, regulatory uncertainties, and security concerns. These conflicting arguments highlight the multifaceted nature of the cryptocurrency and its evolving relationship with the global financial system.
Comparison of Predicted Future to Current Market Position
Bitcoin’s predicted future is often compared to its current market position. Some projections suggest that Bitcoin will experience continued growth and adoption, reaching new highs in the future. Others predict that Bitcoin will remain a niche asset, with limited mainstream adoption. These predictions reflect the ongoing uncertainty surrounding Bitcoin’s future trajectory.
Summary of Perspectives on Bitcoin’s Future
| Perspective | Argument | Likelihood |
|---|---|---|
| Optimistic | Bitcoin’s unique characteristics and potential applications will drive adoption and price appreciation. | Moderate to High |
| Neutral | Bitcoin’s future is uncertain, with both potential for growth and decline, depending on various factors. | Medium |
| Pessimistic | Bitcoin’s inherent volatility and regulatory challenges will limit its adoption and lead to price devaluation. | Low to Moderate |
Last Point
In conclusion, the potential for Bitcoin’s price to reach zero is a multifaceted issue influenced by numerous variables. This discussion highlighted the theoretical scenarios, historical precedents, and alternative perspectives on the cryptocurrency’s future. Ultimately, the outcome remains uncertain, requiring ongoing observation and analysis.
FAQ
What are the key factors that could lead to Bitcoin’s price plummeting to zero?
Several factors could contribute to Bitcoin’s price reaching zero, including widespread adoption of competing cryptocurrencies, significant regulatory crackdowns, or a major security breach that undermines trust in the platform.
How does Bitcoin’s price volatility compare to traditional assets like stocks?
Bitcoin’s price volatility is significantly higher than traditional assets. This inherent instability presents both higher potential rewards and increased risk for investors.
What is the role of blockchain technology in Bitcoin’s potential price collapse?
Blockchain technology, while foundational to Bitcoin, is not immune to vulnerabilities. Security flaws or regulatory pressures could impact Bitcoin’s price if the blockchain is compromised or deemed unsuitable.